Chlorine is the most widely used pool disinfectant. In the swimming pool, there are several types of chlorine: free chlorine, active free chlorine, combined chlorine, or chloramines. We will see here what those different chlorine types mean in the swimming pool. We will also talk about Orp, often used to measure chlorine in a swimming pool.
Disinfected and disinfectant, swimming pool water must be both simultaneously. Disinfected because the pool must not contain viruses, bacteria, or germs. Disinfectant because the pool must be able to eliminate any new element in a short time.
Active Chlorine
Active chlorine is the most important in a swimming pool. The active chlorine ensures that the pool is disinfected, and disinfecting. Active chlorine represents the chlorine molecules available to disinfect organic matter that falls into the water: insects, leaves, dust, etc.
The water must contain between 0.6 and 1.4 mg/L of active chlorine. Beyond that, too much chlorine in the pool and the water will irritate the skin or the respiratory tract.
Active chlorine cannot be measured. There is no test to know the amount of active chlorine in a swimming pool.
The active chlorine level in a swimming pool is different if you use chlorine stabilizer (more info on pool stabilizer here).
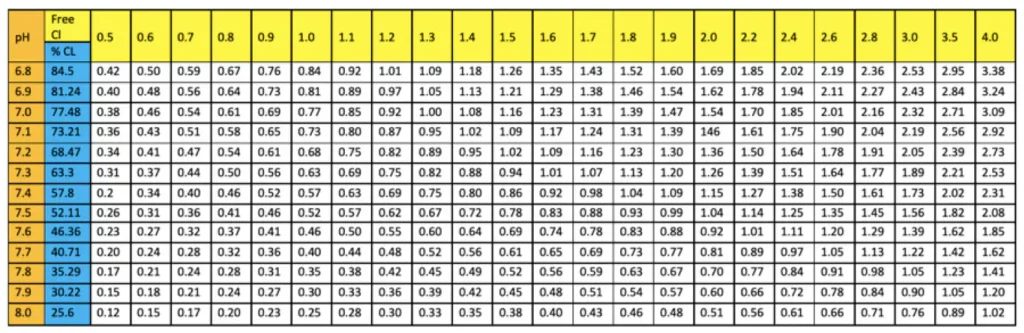
Without chlorine stabilizer. Suppose the pool has no chlorine stabilizer, which is very unlikely. In that case, it is possible to know the quantity of Active Chlorine with a conversion table considering the pH, temperature, and free chlorine level.
Swimming pool with chlorine stabilizer. The chlorine stabilizer modifies the transformation into active chlorine from free chlorine. Therefore, the conversion table cannot be used. There is no way to know the active chlorine in a pool with chlorine stabilizer.
Free chlorine in the pool
Free chlorine corresponds to the chlorine available in the water, which is not yet active. Free chlorine is transformed into active chlorine mainly depending on the pH: the higher the pH, the less free chlorine is transformed into active chlorine. That is why it is often said that chlorine is no longer active with a high pH.
Finally, water hardness, salinity, and temperature also play a role in transforming free chlorine into active chlorine. However, these parameters are often ignored because they are less impactful.
In direct reading, Free Chlorine is therefore not very useful. However, it has a great advantage: it can be measured.
Free chlorine is measured with a reactive chemical test: DPD strips or tablets. The color obtained after the reaction makes it possible to know precisely how much Free Chlorine is in the swimming pool.
Therefore, free chlorine is a measure very often used in swimming pools because it allows you to easily have an idea of the disinfecting power of the swimming pool, provided you have a suitable pH between 6.9 and 7.6.
Swimming pool with chlorine stabilizer. A pool with chlorine stabilizer should always have between 2 and 5 mg/L of free chlorine. Below 2mg/L, bacteria, and algae will grow. Above 5mg/L, the water is too chlorinated and irritates the skin or the respiratory tract. Hence, the recommended free chlorine level in pools is between 2 and 5 mg/L.
Swimming pool without chlorine stabilizer. Use the conversion table to obtain the free active chlorine content.
Combined chlorine, or Chloramines in the pool
Combined Chlorine and Chloramines represent the same thing in the swimming pool. Combined chlorine represents free chlorine neutralizing organic matter. The Free Chlorine came to combine with the organic matter. Therefore, it is no longer free or active because it neutralizes organic matter. It no longer participates in the disinfection of the swimming pool.
Chlorine in a swimming pool is a bit like cops and robbers:
- Free chlorine is the cop who monitors the area
- Organic matter like leaves, bacteria, insects, sweat are the robbers
- As soon as the organic matter (the robber) enters the water, the free chlorine (the cop) comes to neutralize them
- When the organic matter is neutralized, chlorine is no longer available. They form combined chlorine, chloramines, in the swimming pool.
Chloramines smell bad. They are the ones who create the smell of chlorine in a swimming pool. The more a pool smells of chlorine, the more chloramines it contains. Hence, a swimming pool that smells of chlorine is a terrible sign.
A swimming pool must always have less than 0.6 mg/L of combined chlorine or chloramines. Above this rate, the swimming pool is then polluted by chloramines, and they must be eliminated.
Eliminate chloramines
Chloramines are eliminated by carrying out a super-chlorination operation or pool shock.
We will add a large quantity of chlorine to reach approximately 10mg/L. The very high rate of chlorine will release the chloramines, and the organic matter transformed into ammonia, nitrogens, or phosphates will evaporate.
It is then necessary to wait several hours for the chlorine level to go down and stabilize.
Total Chlorine
Total chlorine represents the sum of Free Chlorine and Combined Chlorine.
Total chlorine = Free Chlorine + Combined Chlorine
It is a useless measure in a pool.
However, it is not always possible to measure Combined Chlorine, while Free Chlorine and Chlorine can be measured more easily. In these cases, this formula is used to determine the Combined Chlorine.
Total chlorine is also measured with a reactive chemical test such as DPD strips or tablets.
Pool Orp and Chlorine
The ORP represents the potential of oxidation-reduction of the water in a swimming pool. It directly shows the disinfectant capacity of the water, i.e., the active chlorine content for a chlorine pool.
The advantage of ORP is that it is measured electronically with a probe. All electronic testers and salt-chlorine generators use this measure.
The ORP also works with chlorine, salt, or bromine pools because it does not seek a molecule but a disinfectant capacity.
We saw that the Active Chlorine was less present with a pH, and therefore the water was less disinfectant. This behavior can be observed with ORP measurement of the swimming pool: when the pH, the ORP decreases.
Therefore, it is a very reliable indicator for the swimming pool. However, it has some drawbacks. Too high a chlorine stabilizer level can distort the results in a pool.
The ORP gives a measurement in mV. In a private pool, you must target an ORP level between 650mV and 750mV.
Below 650mV, the pool is not disinfecting enough: the pH must be lowered, or the chlorine must be increased.
Above 750mV, the pool is too aggressive and could irritate the skin. You have to raise the pH and/or lower the chlorine.
